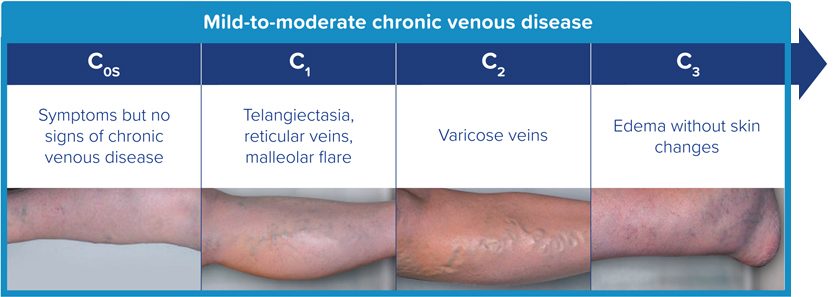
WHAT ISMILD-TO-MODERATE
CHRONIC VENOUS DISEASE?1
A condition caused by poor blood circulation in your legs, which may lead to signs and symptoms like1,4:
Risk factors you can control…4,5

STANDING FOR LONG PERIODS

OVERWEIGHT
Risk factors you can control…4,5

STANDING FOR LONG PERIODS

OVERWEIGHT
…and those you can’t 4,5

Affects more women than men

Increased risk after 35

FAMILY HISTORY
…and those you can’t 4,5

Affects more women than men

Increased risk after 35

FAMILY HISTORY
Discover Venixxa®
- A treatment option for relief of signs and symptoms of mild-to-moderate chronic venous disease 1
- Used in more than 100 countries for over 30 years
- Helps reduce lower leg swelling and relieve pain, heaviness and functional discomfort 1
Made from citrus bioflavonoids 1,6.
Medicinal ingredient:
Venixxa® (Micronized Purified Flavonoid Fraction [MPFF]) consists of the medicinal ingredient citrus bioflavonoidscontaining 90% diosmin and 10% flavonoids expressed as hesperidin.* 1
Available in pharmacies over-the-counter
Demonstrated effects of Venixxa® vs. Placebo
from baseline to Week 8 in a study of patients with
symptomatic disturbances of the venolymphatic system †,2
Venous functional symptoms (mean scores) 2
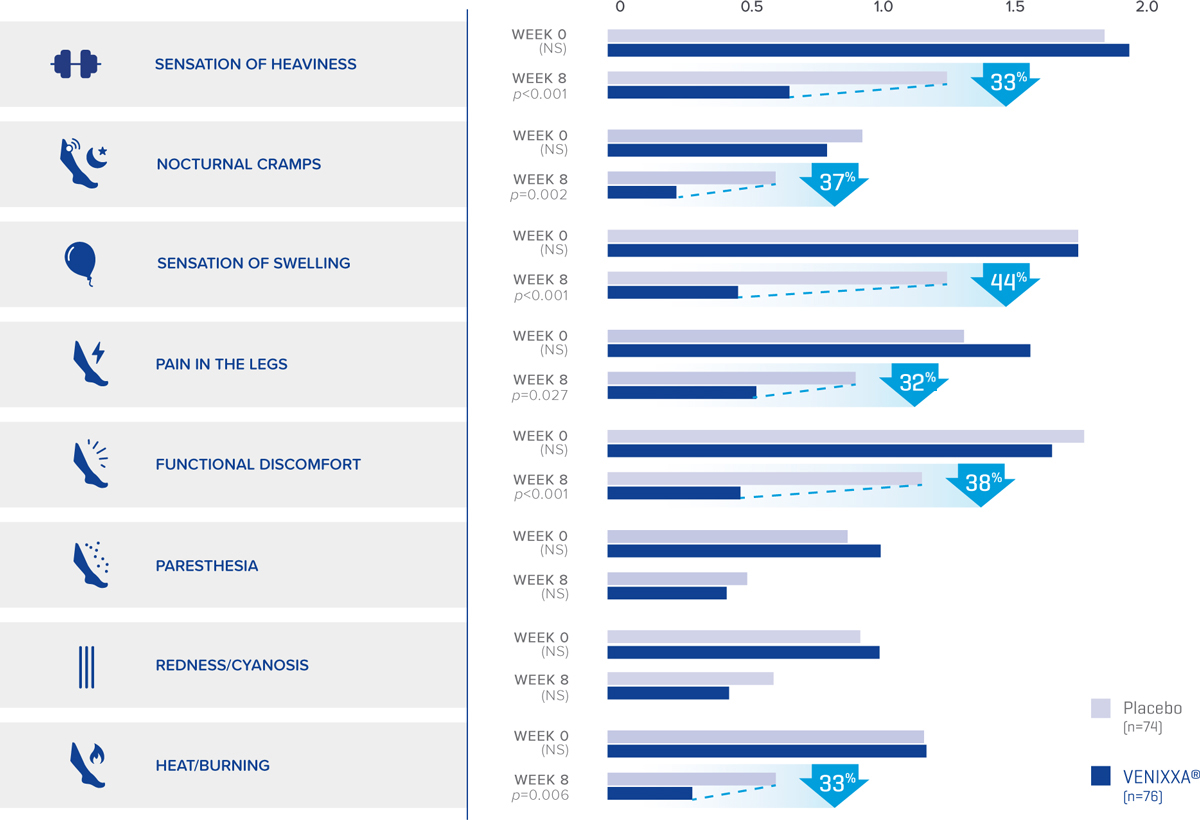
Adapted from Gilly R, et al.2
NS: not significant
Standard deviation (SD) for all data points: ±0.1. Verbal scale used: 0, no symptoms; 1, moderate symptoms without repercussion on daily activities; 2, appreciable symptoms but allowing daily activities; 3, severe symptoms causing discomfort or hampering daily activities.
†Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study on 160 outpatients who received either MPFF 500 mg (450 mg diosmin + 50 mg hesperidin; n=80) or placebo (n=80) twice daily for 8 weeks. Venixxa® is not indicated for use in relieving/reducing all of these symptoms.
Recommended Dosing1
Treatment for mild-to-moderate
chronic venous disease



If response is inadequate or unsatisfactory after 2 months, reconsider diagnosis as edema may have alternative causes 1.

IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION 1
Known adverse reaction
Hypersensitivity/allergy, gastrointestinal discomfort, dizziness, headaches, malaise, and skin reactions have been known to occur; in which case, patients should discontinue use and consult a healthcare practitioner.
Cautions and Warnings
- Treatment should be avoided during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- The patient should be advised to consult a healthcare practitioner:
- if symptoms of chronic venous disease persist or worsen, or in the event of inflammation of the skin, thrombophlebitis or subcutaneous induration, severe pain, ulcers, sudden swelling of one or both legs, cardiac or renal insufficiency or disorder;
- prior to taking prescription medication.
For more information:
See Warnings, Cautions, and Directions of Use at https://health-products.canada.ca/lnhpd-bdpsnh/index-eng.jsp for information to assist in benefit-risk assessment. Always direct the patient to read the label. The Terms of Market Authorization are also available upon request by calling 1-888-902-9700.

®Venixxa is a registered trademark of Servier Canada Inc.
© 2019 Servier Canada Inc.
235, boulevard Armand-Frappier
Laval, QC H7V 4A7 1-888-902-9700


References:
- Venixxa® Product Licence. Servier Canada Inc. 2017.
- Gilly R, Pillion G and Frileux C. Evaluation of a new venoactive micronized flavonoid fraction (S 5682) in symptomatic disturbances of the venolymphatic circulation of the lower limb: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Phlebology. 1994;9:67–70.
- Rabe E. et al. Epidemiology of chronic venous disorders in geographically diverse populations: results from the Vein Consult Program. Int Angiol. 1012;31:105-115
- Bergan J.J., Schmid-Schönbein G.W.,Coleridge Smith P.D., Nicolaides A.N., Michel R. Boisseau M.R. and EklofB., 2006, Mechanism of Disease - Chronic Venous Disease, The NewEngland Journal of Medicine, Massachusetts Medical Society, Boston, pp..488-498
- Raffetto J.D, 2018 , Pathophysiology of ChronicVenous Disease and Venous, Elsevier Inc., Boston, pp. 337-347
Ulcers - GARNER R.C., GARNER J.V., GREGORY S., WHATTAM M., CALAMA., LEONG D., 2002, Comparison of the Absorption of Micronized (DaØon500 1 mg) and Nonmicronized 14 C-Diosmin Tablets After OralAdministration to Healthy Volunteers by Accelerator Mass Spectrometry andLiquid Scintillation Counting, JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICALSCIENCES, VOL. 91, NO. 1, York, pp. 32-40